








Project Overview
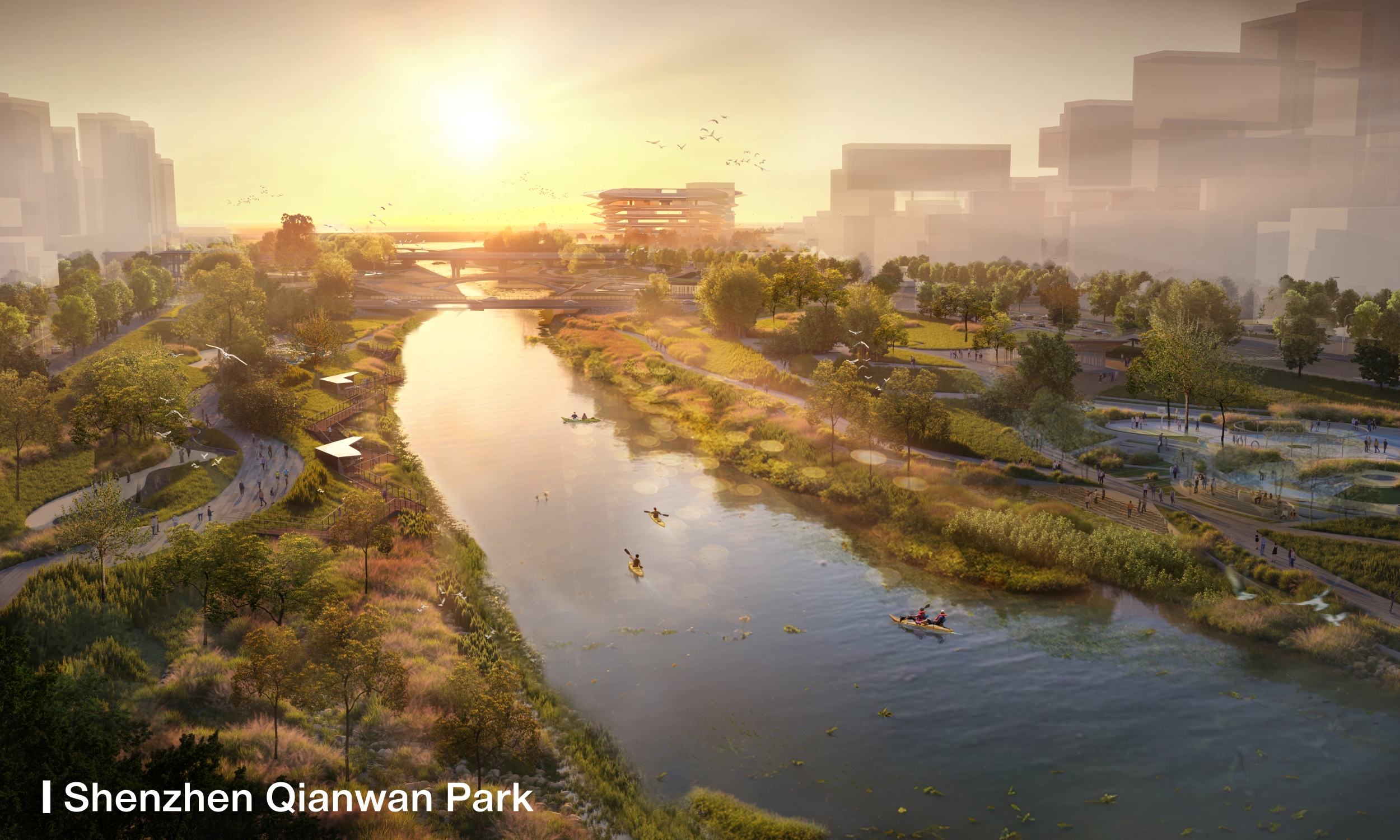
Located in west Shekou Peninsula in Shenzhen, Qianwan Park is strategically located in the main economic axis of the Pearl River Delta region, adjacent to Hong Kong and Macau. Qianwan Park is connected to Qianhai Bay to the west and Dananshan mountain range to the southeast, making it an important component of the Shenzhen urban landscape, where mountains and sea converge.
Qianwan Park will revolve around water as its central theme, enhancing the waterways originating from Nanshan. In the vibrant urban setting of Qianhai, it aims to enrich our quality of life and establish itself as a prominent waterfront destination. The project design concept emphasises ‘dynamic water, vibrant scenery, and embracing diversity’.
The project area mainly attracts young innovators and professionals working and living in the region. Qianwan Park aspires to be a landmark that integrates Lingnan culture while embracing youthful perspectives and respecting nature. The design will preserve traditional culture and incorporate modern amenities, emphasizing sustainability and harmonious integration with the natural environment. To contribute to a sustainable future, the project has set a carbon neutrality goal to be achieved by 2035.
Project Commissioner
Shenzhen Qianhai Construction & Investment Holding Group Co., Ltd
Project Creator
Ove Arup & Partners Hong Kong Limited
Team
Theresa Yeung, Claudia Yu, Xu-Jie Cao, Geng-Bo Wang, Raymond Ho, Eleen Ji, Anna Wong, Jie-Rong Chen, Nemo Liu, Bing-Qing Yu, Ayaan Su, Fischer Yu, Jason Chen, Xiao-Xin Yang, Hana Zhong
Project Brief
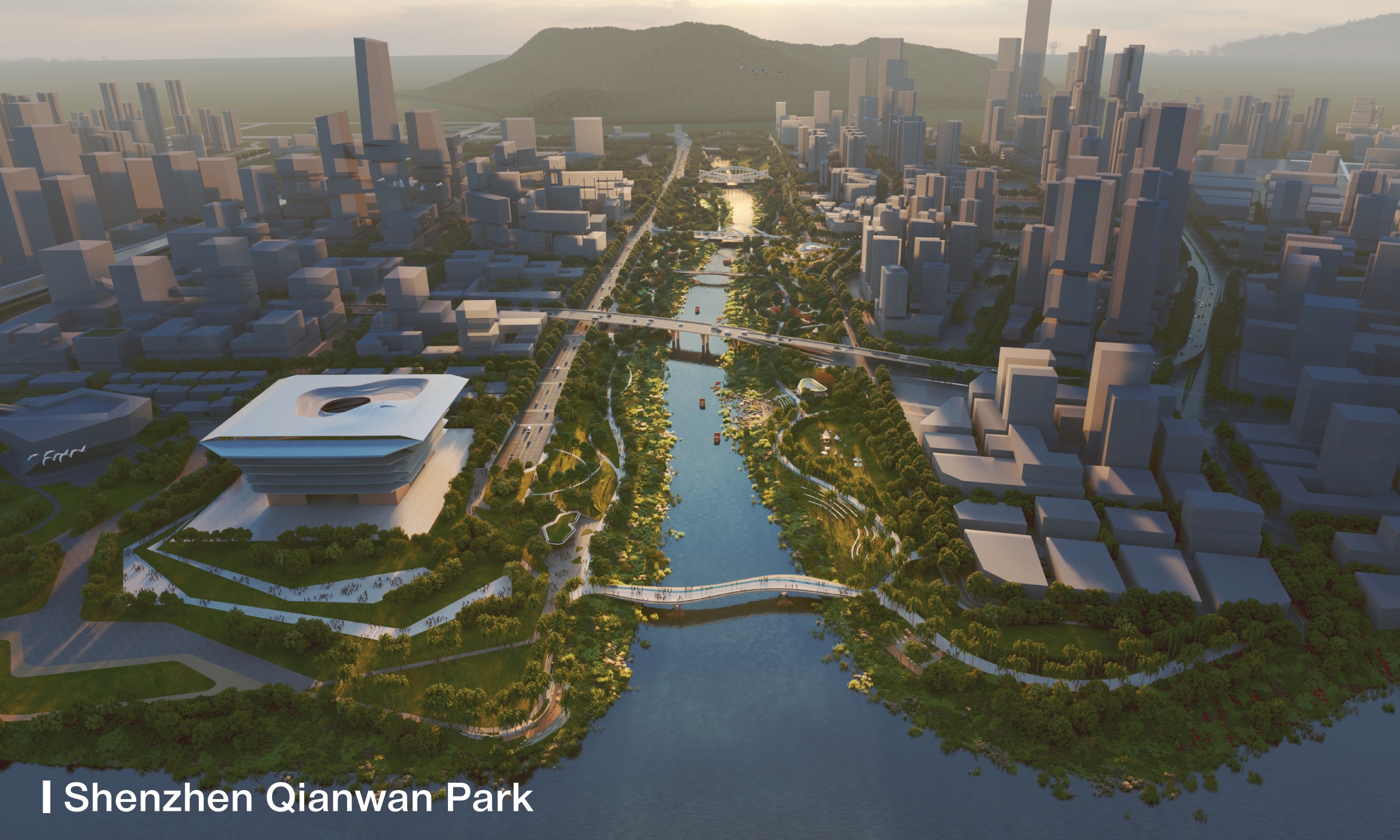
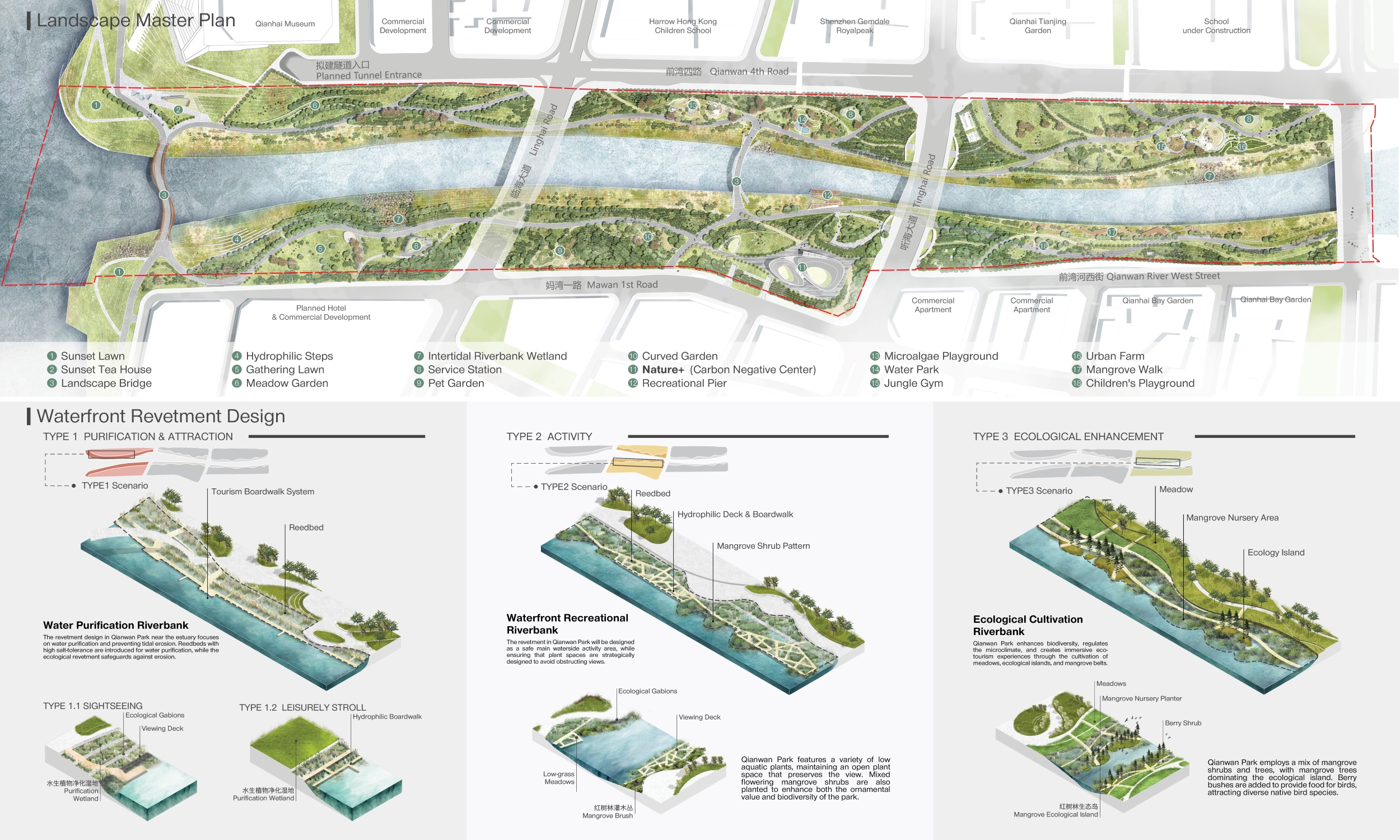
With a total area of 32.4 hectares, Qianwan Park features an International Harbour Gateway, Universal Urban Space, and Ecological Nature Positive Parkland.
Leveraging its landscape and geographical advantages, the Park connects people and integrates innovation into an immersive multi-dimensional natural space, creating a vibrant life experience for the public. It aims to establish a new paradigm for waterfront development that coexists and thrives in harmony with the Qianhai and the Bay Area, featuring an internationally renowned ecological corridor.
The Park boasts a 3km riverfront shoreline designed with diverse waterfront elements, complemented by two landscape footbridges to activate vitality on both sides of the river. With a total of 71% green coverage, the Park offers various art, culture, and dining facilities ensuring a wide range of recreational experiences. It also provides a 15,000m2 underground parking space.
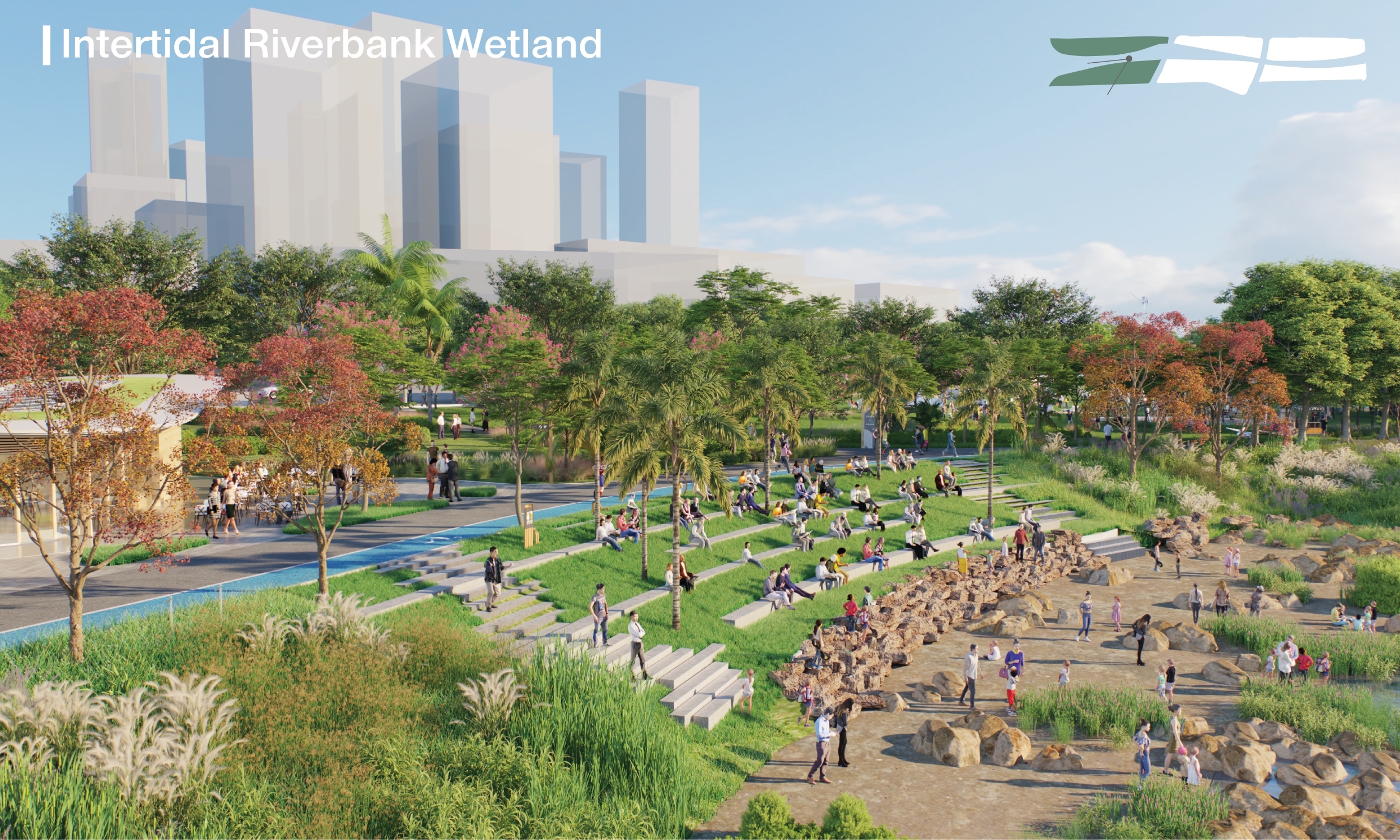
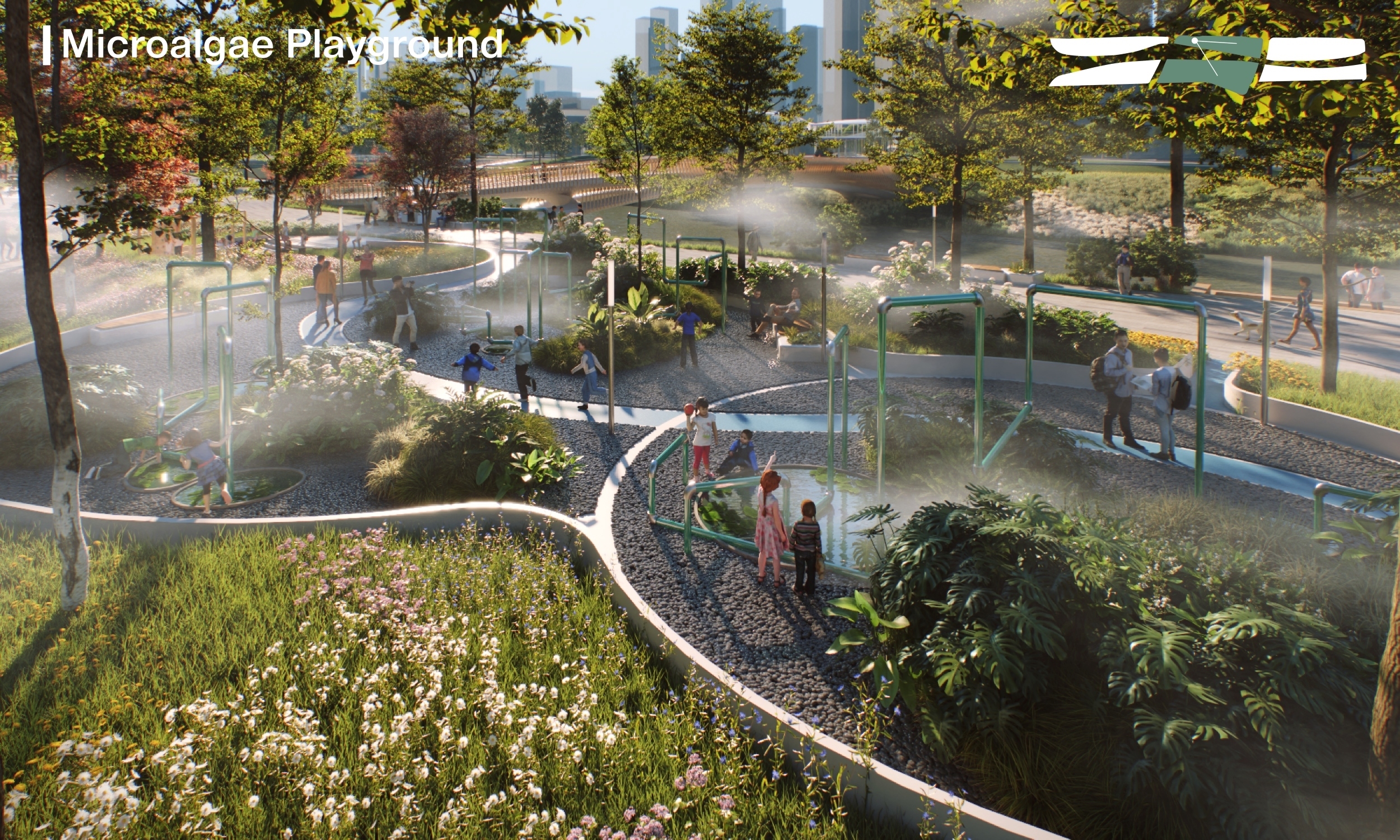
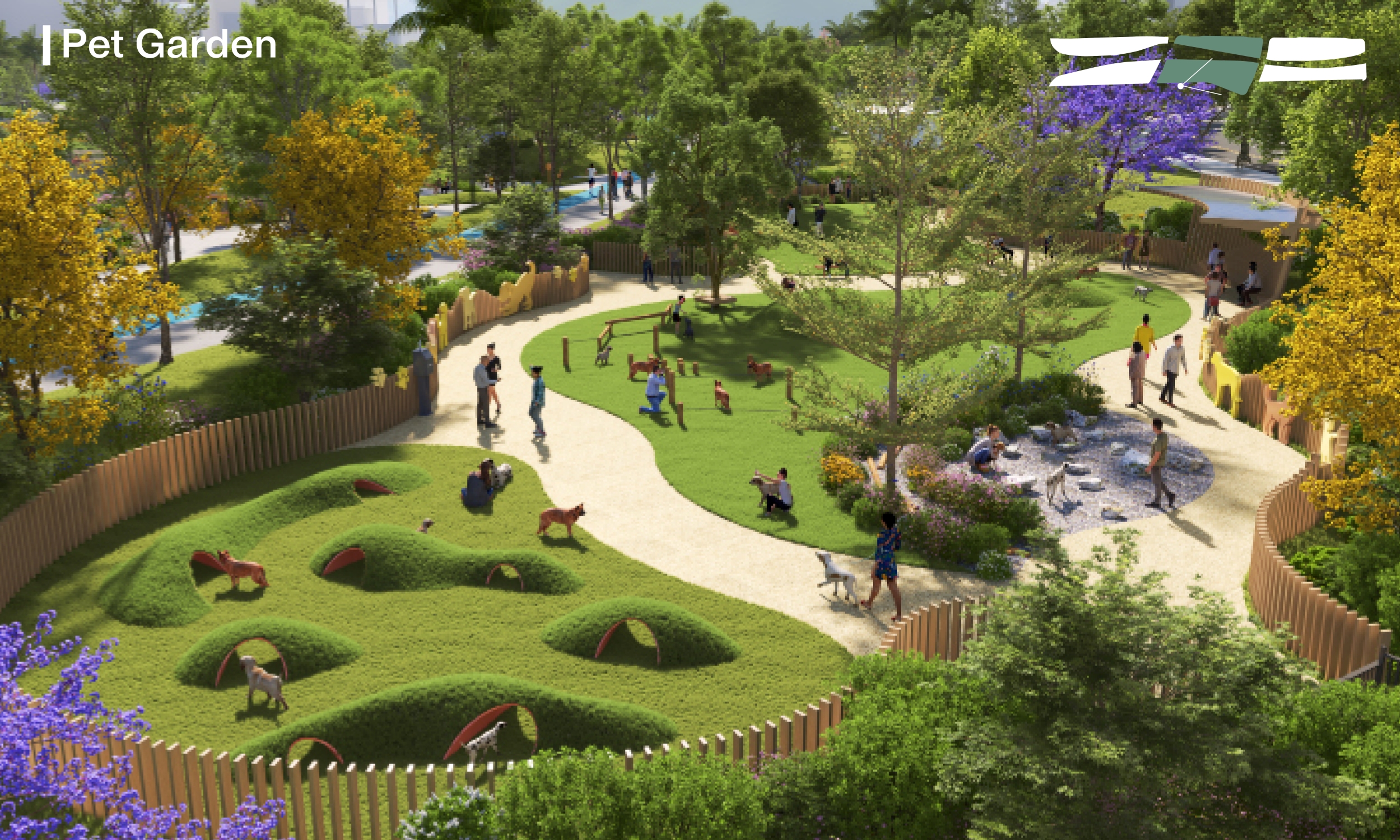
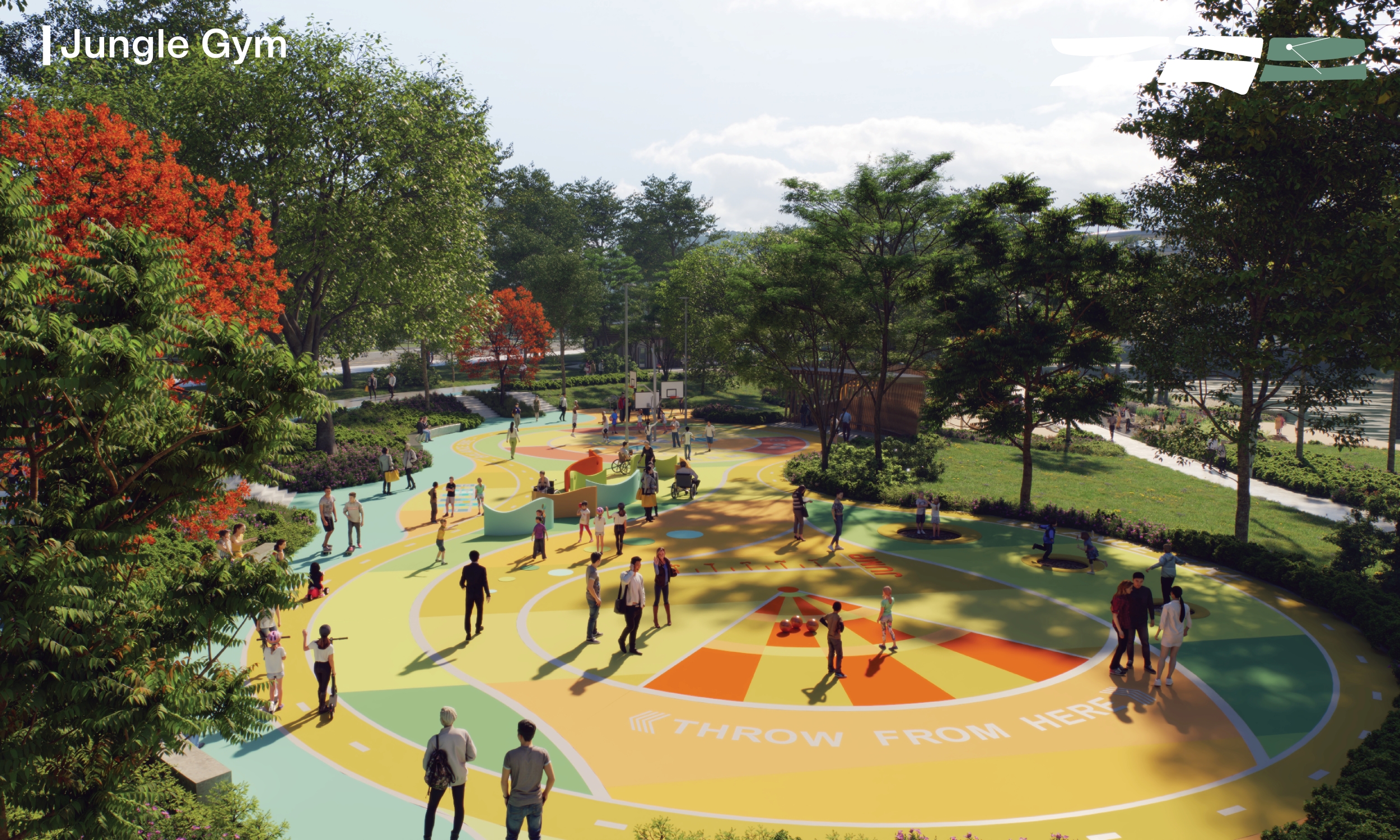
The Park features a diverse landscape, comprising circular enclosed areas, point-opened areas, and linear series areas. This division creates a rich and varied experience throughout. Additionally, the design of the Park prioritises water purification and ecological conservation while emphasising sustainable practices. The Park is divided into four functional zones: ‘Tourism Landscape Zone’, ‘Dynamic Recreation Zone’, ‘Dining Landscape Zone’, and ‘Ecological Education Zone’.
Project Innovation/Need
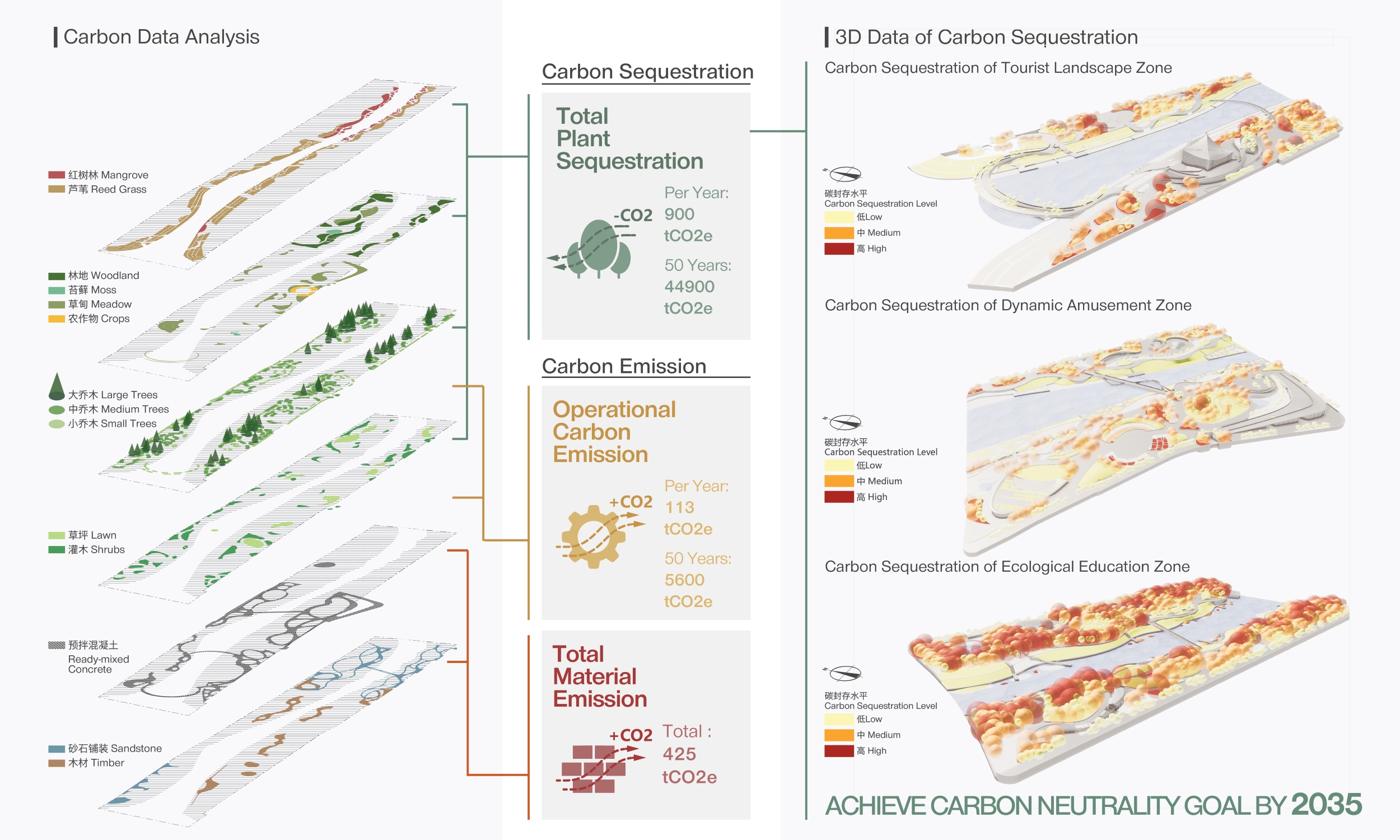
To achieve carbon neutrality by 2035, Qianwan Park targets for an average annual carbon sequestration of 900 tons CO2e, resulting in a cumulative carbon sequestration of 44,900 tons CO2e over 50 years. To assess carbon sequestration and carbon emission, we developed an innovative carbon calculator. This tool generates 3D data of carbon sequestration to visualize the result of carbon sequestration distribution and levels at key areas including ‘Tourist Landscape Zone’, ‘Dynamic Amusement Zone’ and ‘Ecological Education Zone’.
Our carbon data analysis includes three dimensions - plant carbon sequestration, operational carbon emission and embodied carbon emission. Plant carbon sequestration includes water plants and terrestrial plants. To maximize carbon sequestration of the project, we carefully select planting species, opting for high-performance carbon-sequestering varieties. These plants not only help absorb carbon dioxide and purify the air but also provide vital habitats for surrounding organisms. Regarding operational carbon emission, lighting, irrigation and mowing are the parameters. While manufacturing, transportation and installation are the dimensions under embodied carbon emissions.
Design Challenge
In terms of topographical and hydrological constraints, the terrain along the Qianwan River is predominantly flat, with a general elevation of +4.8 meters above present datum (mPD) and an average height difference of 4.4 meters from the riverbed. The gentle slope of the ground makes it challenging to establish a natural water flow path, which consequently constraints the natural discharge and flow of water. This characteristic has been carefully considered when planning and designing water management strategies in the area.
Besides, litter pollution is a concern in estuarine waters. In addition to sediment impurities resulting from natural influences, domestic waste can also be found in the water near the river mouth. This water body is in proximity to a temporary logistics parking lot, and human activities in the area may potentially disturb the water quality.
Riverbank elevation difference is another key issue. Throughout the entire length of the riverbank, there is a noticeable difference in elevation between the water surface and the ground surface, characterized by a slightly steeper slope. This topographical challenge is effectively harnessed and integrated into the design to create ample vertical space and mitigate the impacts of flooding.
Regarding interfaces and road network, although there are existing road networks and pedestrian paths, connection and connectivity between the Park and adjacent urban parcels and major landscape systems should be strengthened.
Sustainability
The principles of sustainability and nature-positive designs are exemplified in the signature landmark building - Nature+ Centre. The building is strategically orientated to maximize area facing the East while minimizing exposure towards the South. Adopted with sunshade measures, such as canopy shading and microalgae facade, the energy consumption of the building can be greatly reduced. Solar panels are installed on top of the curved and undulating roof to increase sunlight absorption. Besides, open space on the top level is vegetated to reduce solar heat gain. The semi-underground carpark allows natural ventilation on both sides and sunlight penetration from above. These design considerations and strategies contribute to a low carbon footprint and a self-sustaining system with zero-net-carbon emission.
The concept of ‘symbiosis’ underpins the ecological enhancement strategies in Qianwan Park. By carefully observing and analyzing the existing ecological conditions, the design integrates riverbanks, waterfront management, and activity areas into a cohesive system that supports each other. Through thoughtful design of terrain structure, vegetation structure, and water management system, the overarching goal is to comprehensively improve the Qianwan River’s ecosystem conditions. This approach ensures a harmonious and sustainable relationship between human activities and the natural environment within the Park.
Landscape Design - Public
This award celebrates creativity and innovation in the use of practical, aesthetic, horticultural, and environmentally sustainability components, taking into account climate, site and orientation, site drainage and irrigation, human and vehicular access, furnishings and lighting.
More Details

